This document provides the network requirements for Oracle RAC 19c installation on a two-node
cluster running Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 9 OR Oracle Linux 9
Prepared for Client Review and Implementations
Note that all IPs and Hostnames in this document are just examples.
Replace it with your environment’s specific IPs.
Network Overview
Oracle RAC 19c cluster environment requires at least two networks:
Public Network (Client Access)
Provides database service access for applications/users.
Typically bonded for redundancy (e.g., bond0 with 2 NICs).
Private Interconnect (Cluster Interconnect) (used for cluster internal communication)
High-speed, low-latency link for RAC heartbeat and cache fusion traffic.
Minimum 10 GbE recommended, dedicated switch or VLAN.
Redundant configuration (2 NICs , no bonding or teaming or virtualization required for private network NICs, as Oracle Clusterware addresses and manages failover/load balancing across them).
Optional Backup Network
For RMAN backups or Data Guard traffic (optional).
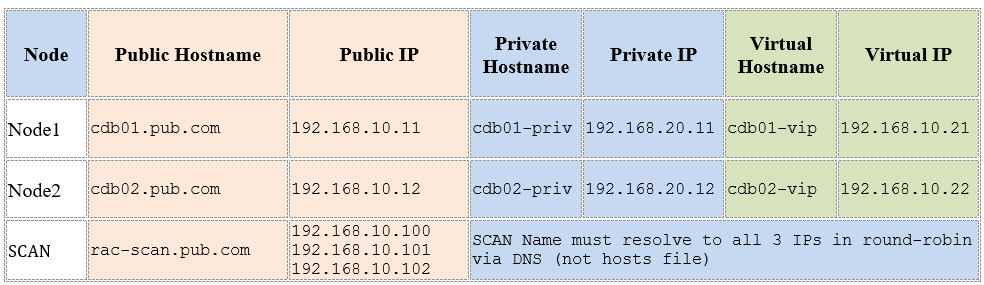
2. Hostnames and IP Addresses
Example configuration (adjust to client environment):
3. Switches and Network Requirements
Public Network Switches:
Redundant enterprise switches (Layer 2/3).
Must connect all public NICs from RAC nodes.
VLAN segmentation supported.
Public NICs must be bonded/teamed for HA.
Private Interconnect Switches:
Interconnect:
Each node should have at least one dedicated network interface for the private interconnect (cluster heartbeat and RAC cache fusion traffic).
For redundancy, Oracle recommends two independent NICs, each connected to a dedicated switch. Oracle’s Highly Available IP (HAIP) configuration automatically load-balances across available private interfaces.
Private interconnects must be on their own IP subnet and not mixed with public client traffic.
Switch Requirements:
Minimum switch speed: 1 Gbps, with 10 Gbps or higher recommended for performance.
Dedicated redundant 10 GbE switches (non-routed) .
No spanning tree, no firewall rules, no routing.
Jumbo frames enabled (MTU 9000 recommended), if supported by all switch hardware and NICs.
Switches should not have VLANs routed outside the RAC subnet and must not introduce latency or packet loss.
No bonding, teaming, or virtualization layers are recommended for private NICs—Oracle Clusterware will handle failover/load balancing with native HAIP
DNS Server:
Must resolve Public, Virtual, and SCAN hostnames/IPs.
/etc/hosts file:
Can be used for private names/IPs, but DNS is required for Public, Virtual and SCAN in production.
4. DNS and Hosts File
• DNS must resolve the SCAN name to three distinct IP addresses on the public subnet (using round-robin A records).
• Both public and VIP hostnames should be resolvable in DNS for best management, while private IP hostnames may reside in /etc/hosts.
• RAC configuration verifies name resolution—misconfigured DNS often causes cluster installation issues
Sample /etc/hosts File
Example configuration (/etc/hosts entries for both nodes), in case DNS is not available:
# Public IPs
192.168.10.11 cdb01.pub.com cdb01
192.168.10.12 cdb02.pub.com cdb02
# Virtual IPs (assigned by Oracle Clusterware)
192.168.10.21 cdb01-vip.pub.com cdb01-vip
192.168.10.22 cdb02-vip.pub.com cdb02-vip
# Private Interconnect
192.168.20.11 cdb01-priv
192.168.20.12 cdb02-priv
# SCAN IPs
192.168.10.31 rac-scan.pub.com rac-scan
192.168.10.32 rac-scan.pub.com rac-scan
192.168.10.33 rac-scan.pub.com rac-scan
Network Topology Diagram
+———————+
| Public Net |
| (Bonded NICs) |
+———————+
| |
+——+ +——+
| |
[ Node1 ] [ Node2 ]
cdb01 / VIP cdb02 / VIP
192.168.10.11 192.168.10.12
Private (HAIP, no bonding):
cdb01-priv: 192.168.20.11
cdb02-priv: 192.168.20.12
SCAN: rac-scan (192.168.10.31–33)
5. Oracle RAC Requirements
SCAN Name (3 IPs) must resolve via DNS, not /etc/hosts (except for test setups).
Each node needs Public IP + VIP + Private IP.
Each RAC node must use the same subnet mask and default gateway for the public network.
Virtual IPs (VIPs) are used for client failover. When a node goes down, its VIP fails over to another node.
Private network must not overlap with public network.
Oracle supports IPv4 only (IPv6 requires specific certification).
Redundant NIC bonding strongly recommended (mode 4 / LACP).
Public NICs → OS bonding allowed/recommended.
Private NICs → do NOT bond/team, HAIP manages redundancy.
Up to 4 private NICs can be used by HAIP.
Checklist for Client SYSADMINs
2× NICs for public network (bonded).
2× NICs for private interconnect (bonded, 10 GbE, jumbo frames).
Separate VLANs for public and private networks.
3× SCAN IPs reserved in DNS for rac-scan.pub.com
2× Public IPs + 2× VIPs reserved per node.
2× Private IPs reserved (one per node).
Proper DNS entries for all hostnames.
Switches configured with redundancy, LACP,MTU=9000 on private interconnect.
Firewall rules allow communication across all cluster nodes (public + private).
Correct network configuration is crucial for high availability, failover, and performance of Oracle RAC clusters. Misconfiguration can lead to database outages and slow failover behavior.
Summary
The client should offer:
1. Public IPs, VIPs, and SCAN IPs in DNS
2. Private IPs configured in /etc/hosts
3. Switches with redundancy
4. Segregation of RAC interconnect traffic